Conversational AI helps businesses meet customer expectations without increasing operating expenses, protecting customer satisfaction ratings by providing personalized support even in entirely automated interactions.
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence to streamline routine business processes and offer 24/7 customer service is quickly becoming the new normal.
But making Conversational AI a part of your business communications strategy feels daunting when you’re not sure what it is, how it works, and if it will truly benefit your customer base and employees.
This guide to Conversational AI breaks down the basics, answering common questions about Artificial Intelligence, exploring its pros and cons, and highlighting popular use cases and examples of what it can offer your business.
Quick links:
- What Is Conversational AI?
- How Does Conversational AI Work?
- Components of Conversational AI
- Conversational AI vs Chatbots: What’s the Difference?
- Benefits of Conversational AI
- Conversational AI Examples and Use Cases
- Challenges In Conversational AI
- How To Pick The Right AI Application
- FAQs
What Is Conversational AI?
Conversational AI (Artificial Intelligence) is an automated communications technology using Natural Language Processing and machine learning to engage in two-way conversations with human users.
Artificial Intelligence analyzes and “understands” a speaker’s language, intent, emotions, and conversational context to emulate natural human speech patterns and provide relevant responses.
Unlike pre-programmed automated attendants or standard chatbots, users interacting with Conversational AI-powered applications have a much harder time determining if they’re interacting with a “robot” or a live human agent.
Why?
Because, while basic bots are limited to canned responses, Conversational AI uses machine learning to continually study the way humans actually speak, basing responses on the entirety of a conversation instead of just a few keyword triggers.
Conversational AI imitates the flow of natural conversation to engage in human-like interactions that steadily improve over time and with increased engagement.
Virtual voice assistants like Amazon’s Alexa and Apple’s Siri are some of the best-known IoT (Internet of Things) devices using Conversational AI.
Though Alexa and Siri are primarily for personal use, today’s Conversational AI software provides the same level of automation, assistance, and convenience to users within a business context. Conversational AI applications are available for a variety of business communication channels, including voice calling, SMS texting, chat messaging, email, and more.
Conversational AI tools optimize common business processes like:
- Basic tech support and account management tasks
- Product recommendations, inventory, and order confirmation+tracking
- Billing reminders and bill payment
- Appointment scheduling and management
- Conversational Marketing (lead filtering, data collection, etc.)
- Customer surveys, feedback, employee performance monitoring
How Does Conversational AI Work?
Conversational AI works by initiating a series of analytical processes to understand user intent, generating relevant and context-informed responses, then continually improving itself based on user responses, actions, and reinforcement.
The more you use Conversational AI, the more accurate, personalized, relevant, smarter, and human-like it becomes.
This is all thanks to the algorithm created and improved by Conversation Design–the workflow and architecture behind the best AI-powered conversations.
As you’ve probably guessed, Conversation Design is an incredibly complex topic that includes data collection, language and intent analysis, speech patterns, psychology, KPIs and customer journey mapping, buyer personas, technology, and more.
Components of Conversational AI
Conversational AI is made up of two main components: Machine Learning (ML) and Natural Language Processing (NLP.)
What Is Natural Language Processing?
Natural Language Processing is an AI technology that analyzes what humans mean–both the words they’re saying and the intentions behind them–when interacting with an AI application.
NLP is dedicated to the study of “natural language,” meaning it helps computers understand everything that makes up a conversation: context from previous communications, speech recognition, speaker sentiment analysis, named entity recognition, word sense disambiguation, part of speech analysis, etc.
Natural Language Processing enables humans to speak as they normally would–using basic slang or abbreviations, expressing things colloquially and with emotions, or varying speech tones and speeds.
For example, let’s say a customer calls their bank’s Conversational AI-powered hotline with a question about their account value. They may phrase that question as, “How much money do I have in my account?”, “What is my current balance?” or “How much cash do I have right now?”
Regardless of which way they ask the question, the AI app will provide the same answer–because NLP understands the intent behind the question, not just the words used.
What Is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning is a component of AI that relies on repetition and reinforcement from data input, statistics, and algorithms–not manual human input–to continuously “teach” computers how to provide the most accurate and helpful information.
Machine Learning is what lets Conversational AI applications improve over time.
If you’ve ever asked Amazon’s Alexa a question and received a response, Alexa may ask you, “Was this helpful?” or “Did that answer your question?”
That’s because Alexa–and any device using Conversational AI–is using machine learning to evaluate the quality, helpfulness, and accuracy of the answers it provides. It processes user feedback and adjusts future responses accordingly—even taking current events, behavioral patterns, and personal preferences into account.
Machine Learning and Natural Language Processing contain several components to execute and improve the Conversational AI process.
Let’s break down the Conversational AI process step-by-step.
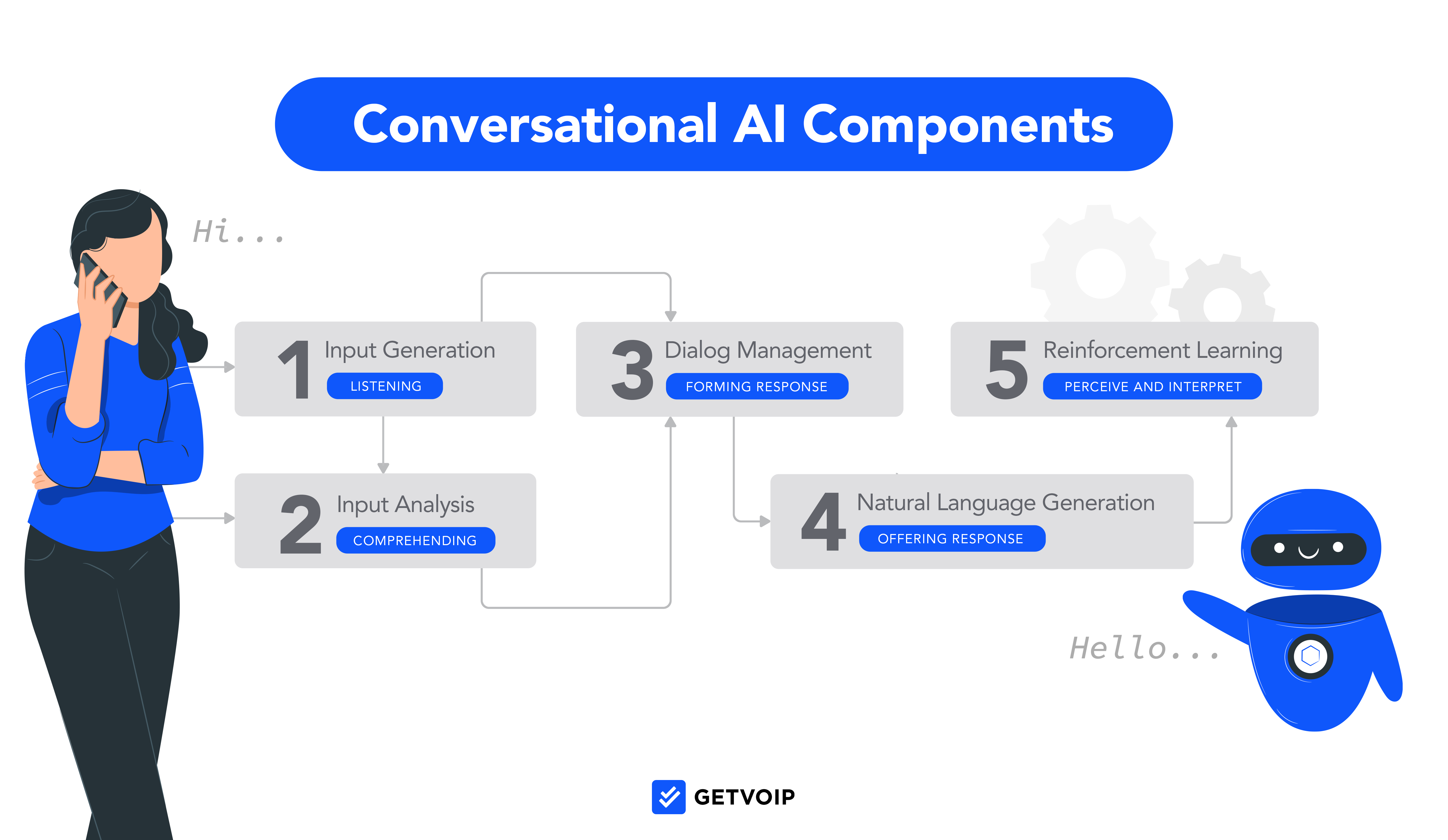
Step One: Input Generation
During the input generation phase, users speak or type their first phrase, comment, or question into the AI application, which could be a business website, social media page, in-app messaging tool, or phone support hotline.
Step Two: Input Analysis
Once the user is finished speaking or typing, the input analysis phase of listening and understanding begins.
First, Natural Language Processing (listening phase) determines the language used, whether it was spoken or typed, and the general meaning of what was said.
Then, Natural Language Understanding, or NLU, (understanding phase) evaluates the conversation’s context to determine the likely intent behind the user’s choice of words.
Voice-based interactions use both NLU and Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) to analyze what the user said and translate their words into text the computer can “understand.”
Step Three: Dialogue Management
During the Dialogue Management phase, the Conversational AI application formulates an appropriate response according to its most accurate understanding of what was said–which, remember, is always improving.
Step Four: Natural Language Generation
While NLP evaluates what the user said, Natural Language Generation (NLG), develops and delivers appropriate responses to user questions and communications.
Depending on the selected communication channel, responses are sent via text, text-to-speech, or speech synthesis (automatically generated speech.)
Step Five: Reinforcement Learning
The final phase of Conversational AI is reinforcement learning (or deep learning.)
This is the machine learning component of the process, where the application evaluates the user’s responses and reactions to the information it provided. These reactions are stored to improve future human-AI customer interactions.
Conversational AI vs Chatbots: What’s the Difference?
Whether or not chatbots are a type of “Conversational AI” is a popular debate in AI and business software spaces.
Chatbots providing a Conversational experience are more sophisticated and “lifelike” than standard chatbots, which can only provide the answers they’ve been programmed with.
The table below further explores the differences between chatbots vs Conversational AI.
| Chatbots | Conversational AI | |
| How Responses Are Created | Rules-based responses via coding, keywords, if/then scenarios, and scripts | Automated Speech Recognition, Natural Language Processing/Understanding, Dialogue Management, Natural Language Generation, and machine learning |
| Level Of Support | General support only, limited by data included in scripts/code | High-level personalized support informed by past and current conversations |
| Level of Understanding | Only responds to pre-programmed keywords, triggers, and phrases, cannot understand variations, natural language, or multiple languages | Users can speak naturally, use international languages, ans different ways, and make spelling mistakes |
| Available Support Channels | Chat messaging only | Voice and text-based channels (Chat, social media messaging, voice calling, SMS, email, etc.) |
| Scalability | Requires complex and time-consuming manual back-end updates | Highly scalable via tier-based pricing and add-ons, integrates with existing business software |
| Support Is | Q&A-based | Conversation-based |
Benefits of Conversational AI
About 34% of marketing and sales business leaders say leveraging Artificial Intelligence will be the biggest factor in improving the overall customer experience.
Given that conversational AI decreases customer wait times, increases first contact resolution rates, eliminates human error, and prevents major miscommunications, it’s easy to understand why.
AI also lowers agent burnout, increasing employee retention rates and job satisfaction.
Additional Conversational AI benefits include:
24/7 Omnichannel Customer Self-Service
80% of consumers say their biggest customer service problem is not being able to get immediate assistance when needed.
Conversational AI provides real-time, around-the-clock customer self-service across voice-based and text-based communication channels. Customers can get support on their own schedules and on their preferred channels–and even switch between chat, SMS, social media messaging, and voice calling during a single interaction.
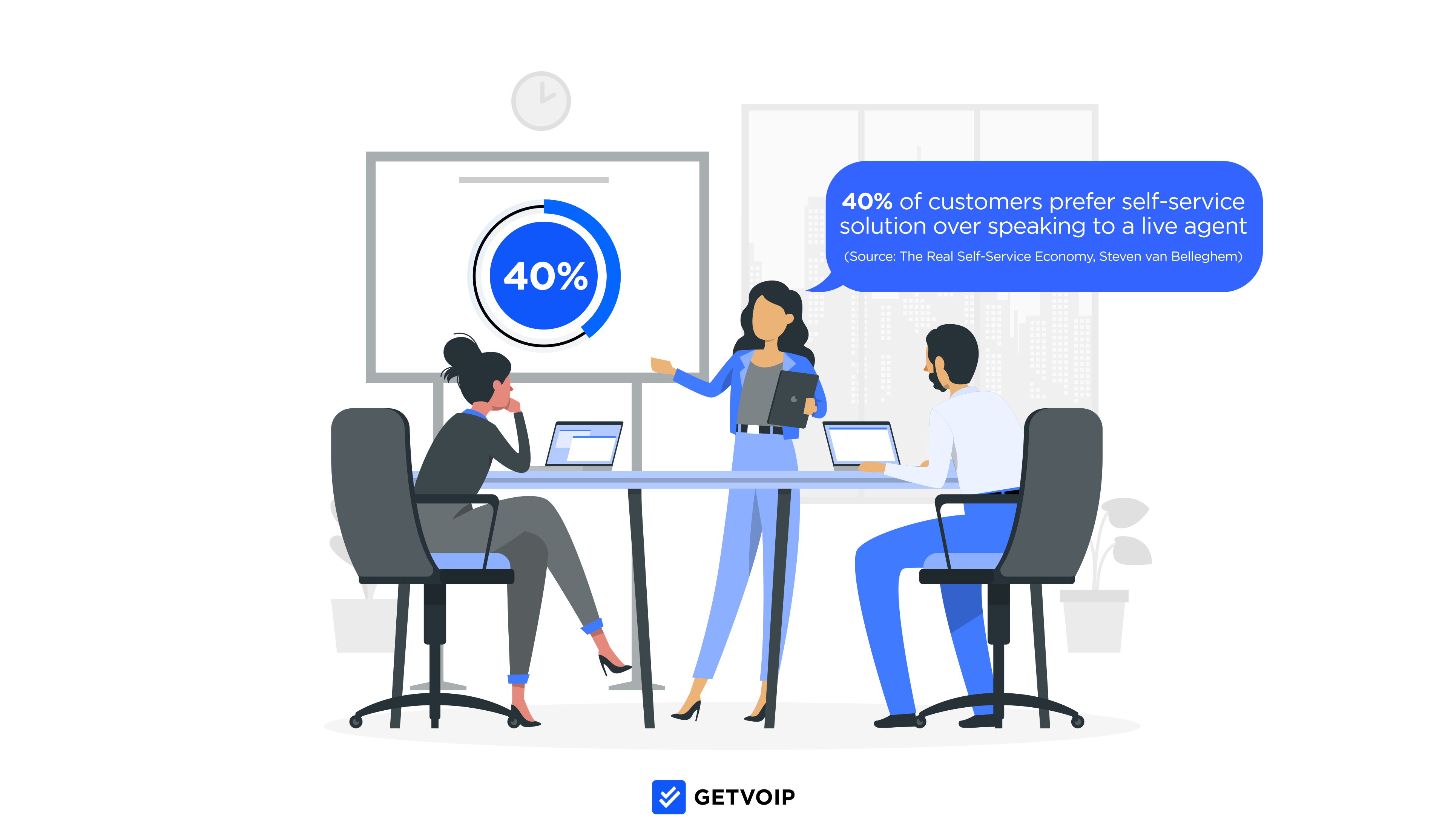
Instead of simply routing calls or chats to available live agents, Conversational AI tools automate the entire customer support process from start to finish (though they can transfer customers to live reps or schedule follow-ups if needed.)
Customer self-service keeps agents free to assist high-level customers, address more complex issues, focus on sales, and boost their productivity as a whole. It also helps businesses avoid the expense of hiring additional agents.
Improved Lead Generation and Increased Sales
Conversational AI revolutionizes the sales process by automating outbound marketing, lead generation and lead qualification, drip marketing campaigns and follow-ups, and even customer opt-outs and DNC databases.
This means improved lead list penetration, more accurate lead scoring, increased revenue, personalized offers and marketing materials, and greater upselling and cross-selling.
Personalized Business Communication
Personalized customer communication increases online conversion rates by at least 8%.
Conversational AI personalizes every customer interaction by automatically pulling customer data from integrated CRM tools and agent notes, referencing past conversations, and creating a natural conversational flow based on customer comments.
Personalized customer service makes consumers feel valued and important, listened to and prioritized, and even creates an emotional connection between customers and businesses.
All of this boosts customer engagement, loyalty, and customer spending.
The more customers interact with your business AI applications, the more data you’ll collect on your customer base. This means more accurate buyer personas, target market research, and customer segmentation.
Anticipate and Evolve With Customer Demands
Human language–just like human wants, needs, and influences–is always in flux.
Conversational AI helps businesses anticipate customer needs, recommend the right products/services, and gain consumer trust.
How?
Because Conversational AI is informed by a much wider context than just a single interaction. When interacting with customers, AI takes into account current market trends, consumer behavioral patterns, cultural influences, geopolitical shifts, current events, and the way our language evolves.
Plus, it collects data straight from the source instead of relying on secondhand research and analysis.
As a result, Conversational AI offers more longevity, value, and ROI than most current business software.
Conversational AI Examples and Use Cases
Below, we’ll take a quick look at some of the best Conversational AI platforms and outline their most popular use cases according to user feedback, AI case studies, and more.
Employee Hiring and Onboarding With Amelia
Amelia is a Conversational AI tool ideal for optimizing hiring and onboarding processes by automating tasks like:
- Screening candidates, resumes, and cover letters, plus identifying talent on job boards
- Interview scheduling, follow-up interviews, and using voice and video analytics to identify top candidates
- Automating background checks
- Creating offer letters and managing employee onboarding documentation
- Creating customized and personalized employee training webinars and programs
- Allowing managers to monitor the training process and new hires via real-time automated alerts, performance monitoring, and in-conversation coaching
Providing Financial Services With Interface.ai
Interface.ai uses Conversational AI and Interactive Intelligence to streamline business operations at banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions with use cases like:
- Suggesting account types and investments based on customer goals and income
- Automating account services/account management (card activation, account closure/opening, balance updates, etc.)
- Sending out fraud alerts, turning card on/off, verifying user identity
- Providing spending breakdowns and basic budgeting suggestions
- Collecting loan/credit card payments, setting up automatic payments
Call Center Optimization With Boost.ai
Boost.ai is a Conversational AI solution especially popular for call and contact centers, assisting with business processes like:
- Lead generation, filtering, and nurturing
- Basic IT support, customer care, and product recommendations via website chatbot
- Market segmentation and automated outbound omnichannel marketing
- Collecting customer feedback and customer surveys
Using Aivo For Retail and eCommerce Businesses
Aivo is a Conversational Commerce platform for online and brick-and-mortar retailers with use cases like:
- Sending order confirmations and real-time order tracking and shipping updates
- Returns processing and user experience management
- Sizing and product recommendations
- Sending cart reminders, in-store event and sales reminders, coupon codes, and loyalty program information
Streamlining HR With IBM Watson
The IBM Watson Conversational AI tool is known for its HR automation capabilities, ideal for streamlining workforce management tasks and other internal business needs like:
- Shift scheduling and bidding
- PTO and vacation requests
- Employee paycheck management
- Sending out company-wide alerts/emergency notifications
- Providing answers to basic company policy questions via chatbots programmed with company documentation/internal knowledge base data
Improving the Patient Experience With Hyro
Hyro is a HIPAA-compliant Conversational AI tool for healthcare providers, and helps automate healthcare-related tasks like:
- Connecting with IoT (Internet of Things) devices to provide remote patient monitoring, alert providers to medical emergencies, etc.
- Helping patients find the right doctor, schedule healthcare appointments/send appointment reminders
- Automatic prescription refills
- Bill payment
- Pre-filling and collecting first time patient forms/information
Amazon Lex For Travel and Hospitality Management
Amazon Lex is a Conversational AI platform with a variety of use cases in the travel and hospitality management sectors, including:
- Hotel booking, confirmation, and suggestions
- Real-time flight updates and flight management
- Itinerary management, tourist site suggestions and ticketing
- Frequent flier mile management
- Room service and amenity requests
Challenges In Conversational AI
Despite the incredible things Conversational AI can do, the technology does face several challenges–none larger than human skepticism regarding user privacy and security.
People fear AI apps will misinterpret and misrepresent them, take actions without consent, record and share private conversations, take their jobs, or one day become sentient and take over the world.
Another less catastrophic–but still frustrating–Conversational AI challenge is the technology’s frequent failure to properly understand what users are saying and what they want.
The dreaded “I don’t know that” response can be caused by unfamiliar accents and dialects, new words, or even by other users that intentionally mislead AI by providing and validating false or useless information.
When this happens, users can rephrase their question, look for help elsewhere, or just keep repeating themselves until they’ve had enough.
Including the option to connect to a live agent when creating IVR system menus and programming chatbots solves these issues.
How To Pick The Right AI Application
While you can create custom AI applications for your business, choosing a pre-built AI platform is easier, faster, and ideal for beginners.
The two main types of Conversational AI Applications are Voice Assistants and Chatbots.
Voice Assistants, or Voicebots, require a corresponding smart speaker and interface. Popular options include Amazon Alexa (Lex for businesses), Google Nest, SmartAisle, Cortana, Kwantics, and Siri.
Voice assistants are best for:
- Brick-and-Mortar Retailers (To create a smart shopping experience)
- Call Centers (To offer 24/7 customer support via IVA Intelligent Virtual Assistants)
- Healthcare Providers (To automate appointment scheduling, insurance management, bill payment, etc.)
- Banks and Financial Institutions (To perform voice-based user authentication, collect payments, provide account updates, etc.)
- Standard Business Process Automation (Real-time call or meeting transcription with post-call and post-meeting summaries, customer account updates, subscription renewal, outbound sales calls, etc.)
Chatbots can be embedded into business websites or business applications to facilitate real-time chat messaging/SMS between customers and team members. Popular options include Ada, IBM Watson Assistant, ChatGPT, and Google Bard.
Chatbots are best for:
- eCommerce Shops (To make product service recommendations, provide shipping/order updates, proactively engage with website visitors etc.)
- IT Support (To automate basic tech support, collect details and account information to prepare agents for live support, etc.)
- Small Businesses and Startups (To maximize agent productivity and keep live agents free by automating basic business tasks)
- Application-based Delivery Services (To protect driver/customer personal contact information and monitor business communications via in-app messaging)
Can’t decide between the two?
Today’s top contact center software providers include pre-built and custom AI chatbots and voicebots to improve CX, streamline workflows, and offer around-the-clock customer self-service.
FAQs
Below, we’ve answered the top Conversational AI FAQs.



